XOR
Basic Overview
|
Description |
Connects two inputs with the logical 'exclusive or' and returns true (1) if exactly one of the input values is true and false (0) otherwise. |
|
Syntax |
XOR('Node1', ‘Node2’) |
|
Parameter |
|
|
Limitations |
Both nodes need to have the same dimensionality, otherwise they will be excluded from the function output. |
Example
Input A =
|
Year |
Value |
|---|---|
|
2019 |
17 |
|
2020 |
0 |
|
2021 |
0 |
|
2022 |
1 |
Input B =
|
Year |
Value |
|---|---|
|
2019 |
1 |
|
2020 |
0 |
|
2021 |
1500 |
|
2022 |
0 |
Output XOR('A','B') =
|
Year |
Value |
|---|---|
|
2019 |
0 |
|
2020 |
0 |
|
2021 |
1 |
|
2022 |
1 |
Limitations
Both input nodes must contain the same levels, otherwise, the function will consider only the more granular function while ignoring the function with fewer levels.
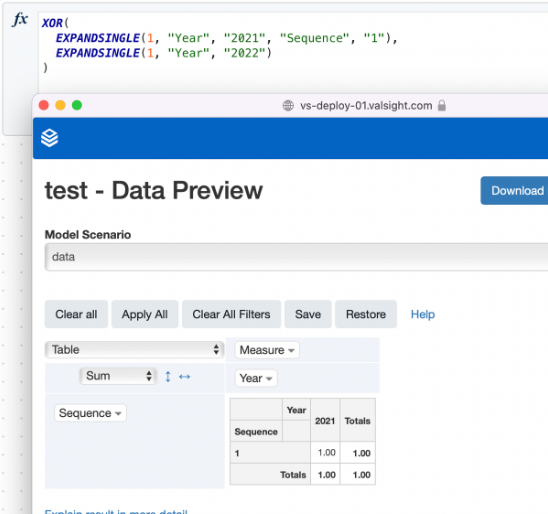
Example of the limitation: The function is given two EXPANDSINGLE() inputs. However, one of the EXPANDSINGLE() functions possesses more levels than the other, resulting in different granularity. The function with more levels is the leading function. This leads to unexpected outputs from the XOR() function.
